Understanding The DPP Law
In the digital age, data protection has become a paramount concern for both businesses and individuals. Rwanda, cognizant of these shifting paradigms, introduced the Data Protection and Privacy (DPP) Law, setting standards and guidelines for businesses operating within its jurisdiction. Ensuring compliance with this comprehensive regulation is not just a legal imperative but a demonstration of a company's commitment to safeguarding its stakeholders' data.
Rwanda's "Data Protection and Privacy (DPP) law" is a rule set up to protect people's personal data. It gives guidelines on how this data can be used, stored, shared, and accessed. And this law says that if a company doesn't follow the rules, they might have to pay a big fine - up to 5% of their sales from the previous year or 1% of their global sales.
According to the guidance of DPO of Rwanda, all organisations should comply with this law if you handle personal data of Rwandan nationals in Rwanda or outside Rwanda that:
Name, location data, HR records, IP address, Phone number, email address, photo, ID number(identification number, national ID cards, drivers licenses, passports, etc.), A/C number(Back account number)
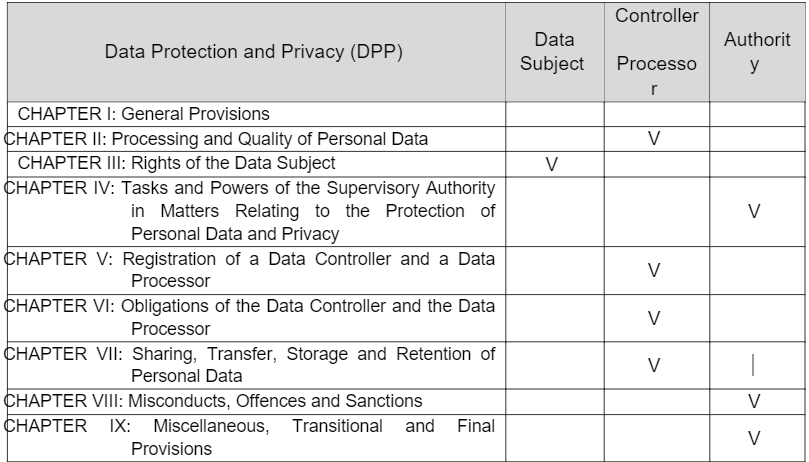
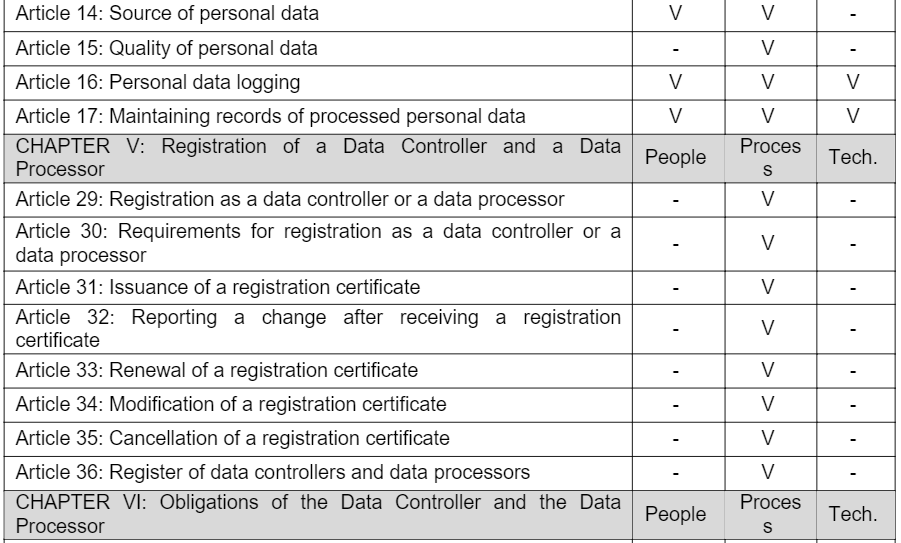
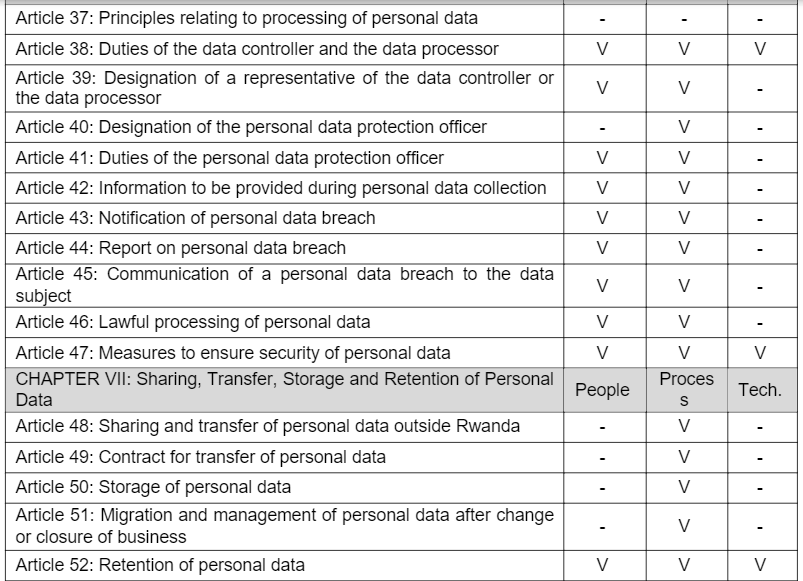
When looking at the 9 chapters of this law, the main players are the Data Subject, Data Controller/Processor, and Authority. From the analysis, the chapters that directly impact the Data Controller/Processor are II, V, VI, and VII.
The PPT Framework: A Comprehensive Approach
Chapters II, V, VI, and VII have been identified as directly relevant to Data Controllers and Processors. The next step involves examining the detailed requirements in each of these chapters for compliance. Some of these requirements call for technical solutions, while others require managerial and operational actions. To address these challenges in a straightforward and effective manner, the PPT Framework is recommended.
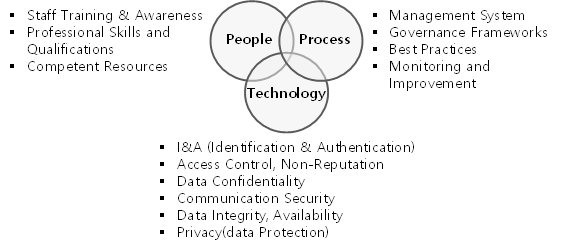
The PPT Framework, standing for People, Process, and Technology, is a great model. It has been utilized across various fields, including cybersecurity, to help organisations adapt and projects succeed by harmonizing these three pillars:
- People: This emphasizes educating staff on the importance of protecting personal data.
- Process: This entails establishing clear guidelines and procedures for processing personal data.
- Technology: This involves using appropriate tools and systems to ensure the security of personal data
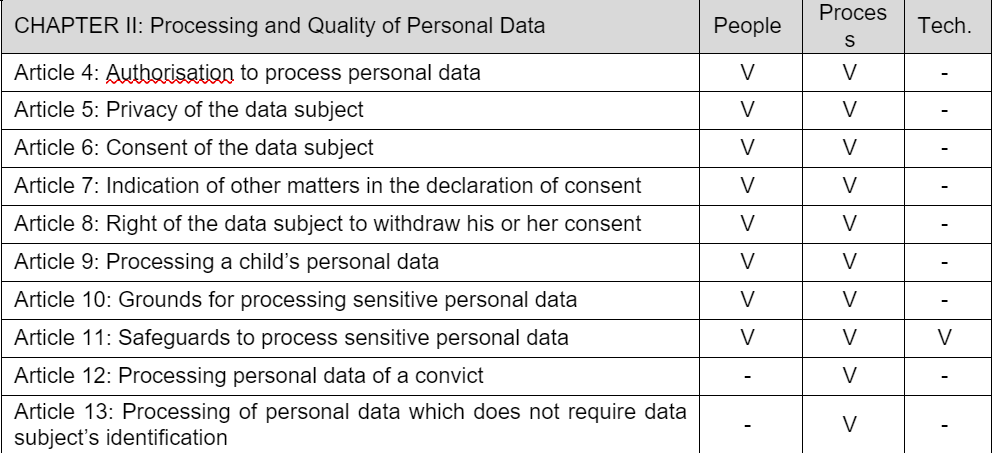
 Based on the PPT Framework, when dividing the specific requirements in Chapters II, V, VI, and VII of the DPP Law into the People, Process, and Technology part, the following table is derived. Examining this table reveals that the 'Process' part encompasses the majority with 37 articles. The 'People' part contains 21 articles, while the 'Technology' part has the least with only 6 articles. However, since most of the legal articles in the technology part imply various detailed requirements, it is necessary to understand the detailed requirements of each legal article.
Based on the PPT Framework, when dividing the specific requirements in Chapters II, V, VI, and VII of the DPP Law into the People, Process, and Technology part, the following table is derived. Examining this table reveals that the 'Process' part encompasses the majority with 37 articles. The 'People' part contains 21 articles, while the 'Technology' part has the least with only 6 articles. However, since most of the legal articles in the technology part imply various detailed requirements, it is necessary to understand the detailed requirements of each legal article.
People & Policy: Building a Strong Foundation
The People & Process Part stands at the heart of the law, laying down the basic and most central rules. It serves as the foundational cornerstone, dictating how organisations should manage and handle personal data. For Data Controllers and Processors, navigating the complexities of the law can be daunting, as almost every provision ties back directly to this pivotal section.
However, compliance isn't a one-off task. Establishing a personal data management system isn’t just a set-it-and-forget-it affair. Instead, it's an ongoing commitment that demands constant attention and upkeep. In the dynamic landscape of data protection, the need for vigilance is paramount. For instance, if there's a data breach, organisations are not only expected but mandated to act swiftly, mitigating the breach's impact. This proactive approach also extends to administrative tasks: when a supervisor makes a request, a prompt response isn't just appreciated—it's required.
To add more weight to these responsibilities, "CHAPTER VIII: MISCONDUCTS, OFFENCES AND SANCTIONS" clearly spells out stringent penalties for any deviations or breaches. The chapter serves as a stern reminder of the legal implications of non-compliance. Handling personal data, especially that of Rwandans, is no small feat. The responsibility and potential repercussions put a substantial burden on all organisations. For Data Controllers and Processors, this is especially significant, emphasizing the importance of stringent compliance and diligence in their operations.
Considering the requirements set by the law, our proposed consulting services for Data Controllers and Processors are as follows.
- DPP Law Compliance Consulting Service
- PIA Consulting Service
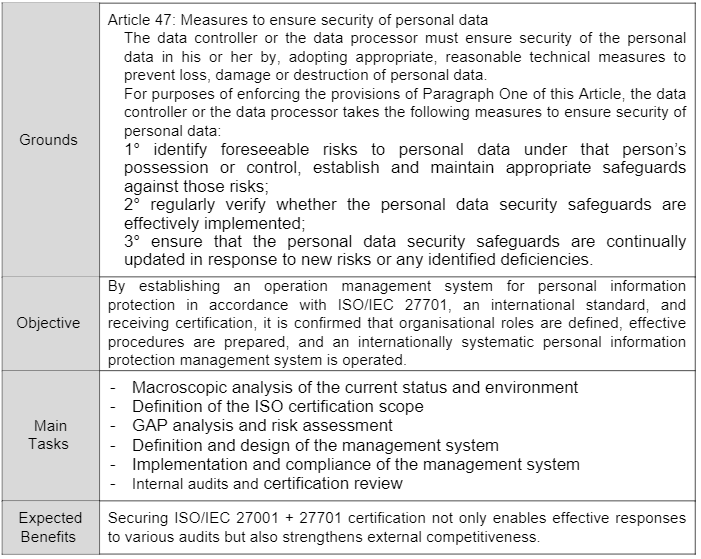
- ISO/IEC 27701 Certificate Consulting Service
- Awareness, Education, Training and Exercise Service
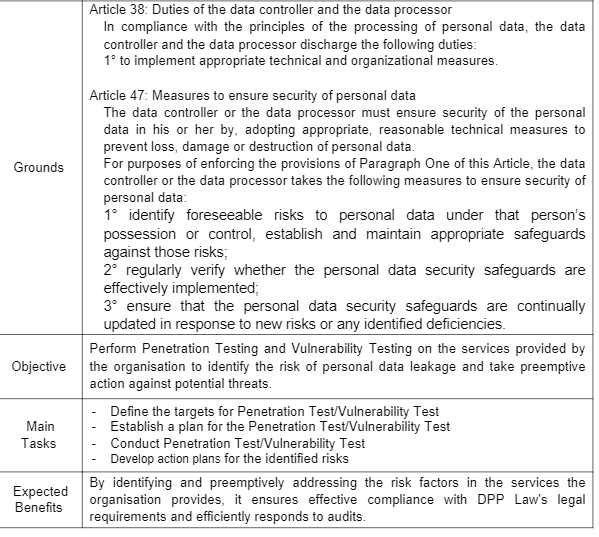
- Penetration Test & Vulnerability Test Service
Please select the consulting services that fit your organisation’s current situation and purpose by referring to the purpose and main contents of the consulting services provided by the company below.



ISO/IEC 27701 Certificate Consulting Service
Awareness, Education, Training and Exercise Service

Penetration test & Vulnerability Test Service
Our company's Cybersecurity Consulting Division not only covers the consulting topics mentioned above but also manages the quality of consulting services by developing methodologies based on years of experience and know-how on various issues related to personal data protection. We assure you that these methodologies, experiences, and expertise will not only help your organisation comply with the DPP Law but will also provide substantial assistance in the actual operation and management of personal data protection.

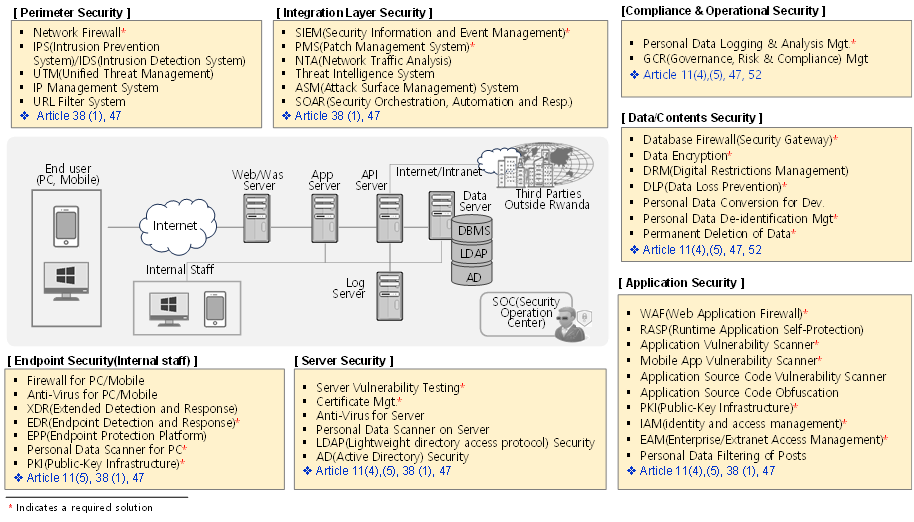
Technology: Securing Data the Right Way
For a long time, many experts have said that the real implementation of the Defense In Depth concept can be achieved through a Multi-Layered Security Strategy. At our company, WiKi Security Corporation's R&D Center, we've developed a security solution matrix for each layer of the Multi-Layered Security Strategy. We continually update and manage this with new technologies.

Based on our Multi-Layered Security Matrix, if we examine the security solutions required in the Technology part for Data Controllers and Processors under the DPP Law, the picture and table below illustrate this.
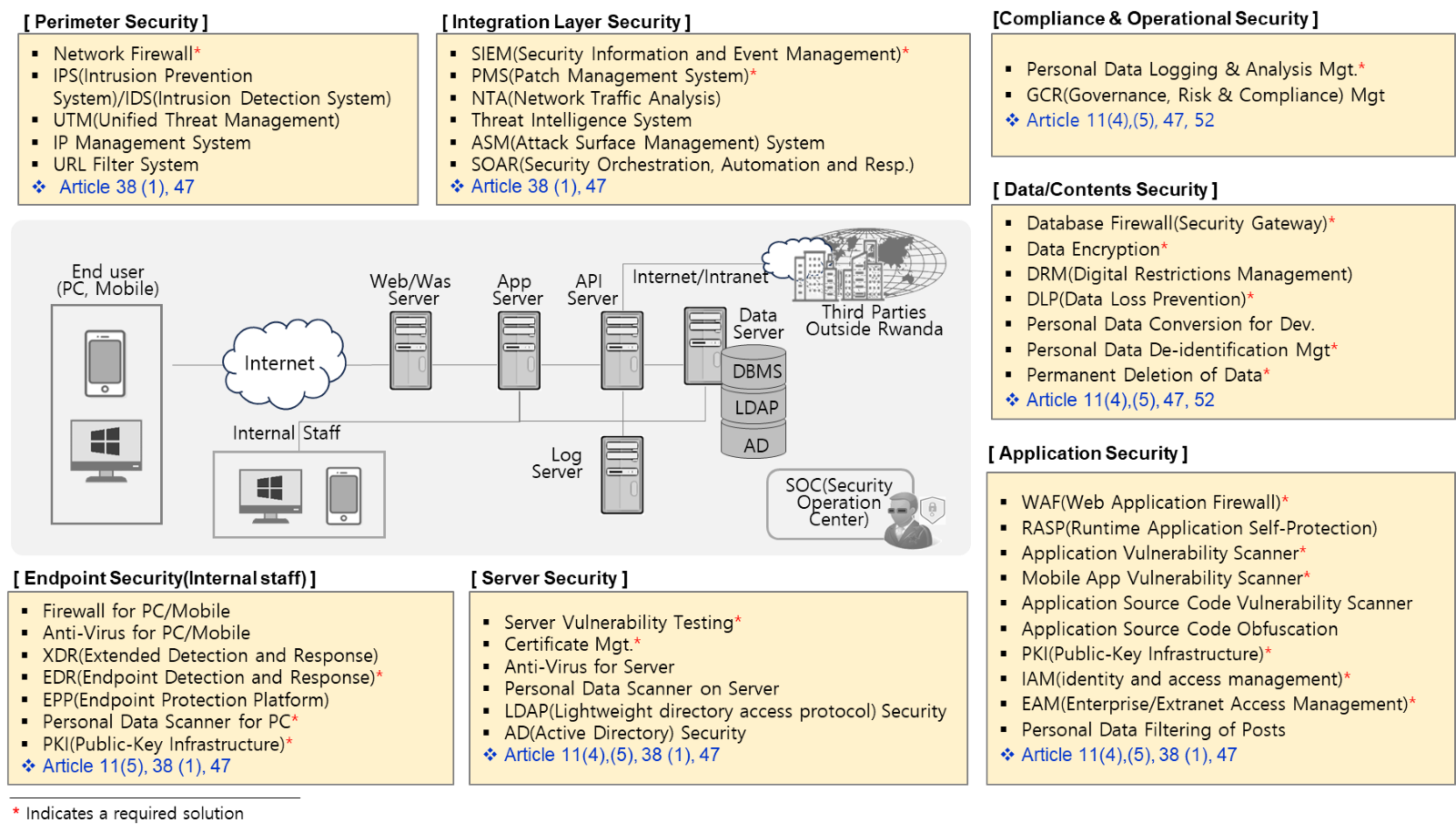
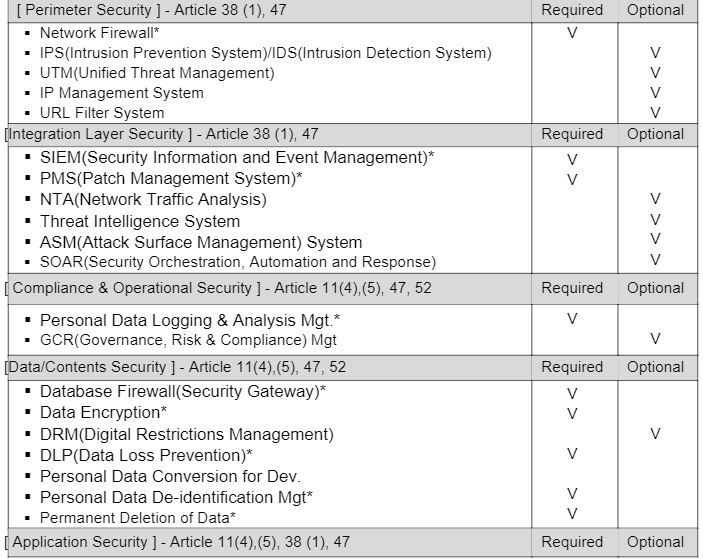
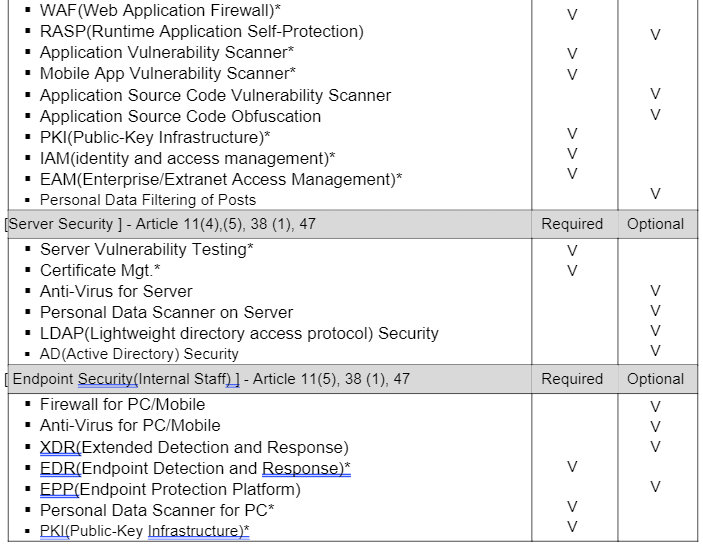
Conclusion: Partnering for a Compliant Future
DPP Law doesn't specifically mention "Data Protection by Design and by Default" which is defined in ISO/IEC 29134 and the EU's GDPR. This is unfortunate, especially since there aren't enough guidelines to help follow the DPP Law. However, since DPP Law is still new, we expect it to improve as it's put into practice and any issues are addressed.
In today's rapidly evolving data landscape, understanding and complying with regulations like Rwanda's DPP Law is crucial. But more than just ticking off a checklist, it's about fostering trust. For Data Controllers and Processors, trust is a cornerstone of operations – ensuring clients and users that their personal data is in safe hands.
We've journeyed through the intricate facets of the DPP Law and explored how the PPT framework plays a pivotal role in ensuring that companies remain compliant. Furthermore, by breaking down the complexities into tangible services and solutions - from endpoint security to perimeter security - we've highlighted the roadmap to a safer, more secure data environment.
Yet, achieving this compliance isn't a solitary journey. It requires collaboration, understanding, and the right partners by your side. As we step into this future together, we emphasize the importance of a shared vision: one where the rights of individuals are respected, and data is protected diligently.
Next Steps: Getting Started with Our Comprehensive Strategy
1. Assessment:
Begin with a comprehensive assessment of your current data processing and handling practices. This will establish where you stand in terms of DPP Law compliance.
2. Consultation:
Engage with our expert team to delve deeper into areas that require immediate attention. We bring a wealth of experience in the domains of People, Process, and Technology.
3. Implementation: Whether it's enhancing staff training, refining processes, or deploying state-of-the-art technological solutions, we guide you every step of the way.
4. Continuous Monitoring & Improvement: Compliance isn't a one-time feat. With evolving laws and threats, it's vital to stay updated. We're here to ensure that you remain ahead of the curve.
Embarking on this journey might seem daunting, but with the right strategy and partners, you're well-equipped to navigate the challenges ahead. We're here to help, ensuring that you meet the stipulations of the DPP Law while also preparing for a future where data protection is paramount.
Appendix - Technology Part in the DDP Law